Understanding Root Cause Analysis (RCA) in Pharmaceutical Quality Assurance
Introduction
In the pharmaceutical sector, maintaining product quality and adhering to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) is critical. Root Cause Analysis (RCA) serves as a vital strategy to systematically uncover, evaluate, and resolve quality-related challenges, thereby minimizing their recurrence. This methodical process empowers organizations to uphold rigorous standards, rectify deviations, and optimize operational workflows.
Understanding Root Cause Analysis (RCA)
Root Cause Analysis (RCA) is a methodical investigative approach designed to pinpoint the fundamental sources of discrepancies, failures, or non-compliance within quality systems. By isolating these core issues, companies can deploy targeted Corrective and Preventive Actions (CAPA) to reduce future risks and ensure sustained compliance.
Applications of Root Cause Analysis (RCA) in the Pharmaceutical Industry
RCA is extensively applied in pharmaceutical quality management to address issues such as:
- Out-of-Specification (OOS) and Out-of-Trend (OOT) analytical outcomes
- Customer complaints and product returns
- Equipment malfunctions and production anomalies
- Regulatory audit findings and non-compliance incidents
- Failures in stability testing
Roles and Accountability in Root Cause Analysis (RCA)
- Department Leaders & Investigators: Responsible for initiating inquiries, compiling data, and leading collaborative discussions to identify causes.
- Quality Assurance (QA) Department: Oversees the review and approval of investigation outcomes, ensuring CAPA plans are validated and effective.
- Multidisciplinary Teams: Provide diverse expertise from areas like production, R&D, and engineering to ensure holistic problem-solving.
Root Cause Analysis (RCA) Framework and Analytical Techniques
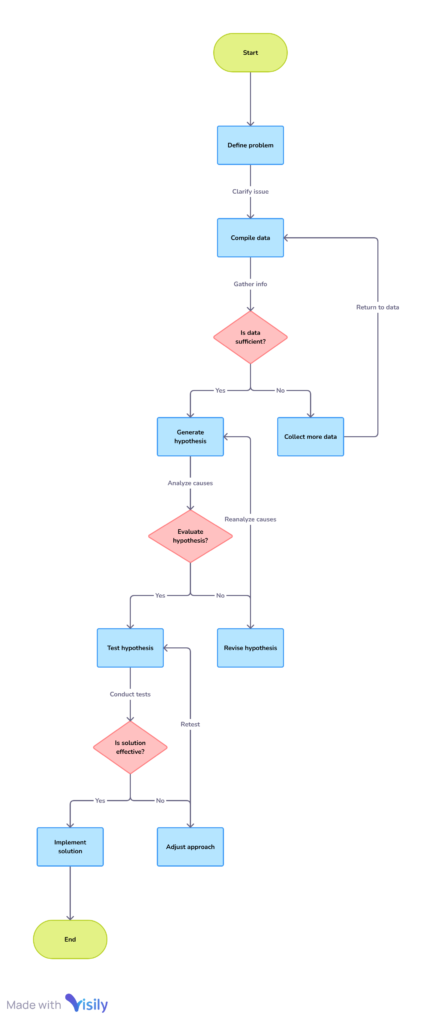
The RCA process involves a series of structured steps supported by specialized tools:
- Defining the Problem: Precisely outline the issue, including specifics like timeline, personnel involved, and environmental factors.
- Data Compilation: Collect pertinent documentation such as batch records, maintenance logs, and historical performance data.
- Hypothesis Generation & Evaluation: Use collaborative methods to list possible causes and validate them against evidence. Key tools include:
- Fishbone Diagram: Organizes potential contributors into categories like personnel, procedures, machinery, materials, and environment.
- 5 Whys Technique: Repeatedly asks “why” to trace an issue back to its origin.
- Fault Tree Analysis: Maps out pathways that could lead to a failure.
- Pareto Chart: Ranks causes by frequency or impact to prioritize actions.
- Control Charts: Track process variability over time to detect trends.
- Root Cause Determination: Validate the most likely cause through data correlation and risk evaluation.
- Risk Evaluation: Assign scores to the severity, likelihood, and detectability of the issue to guide CAPA prioritization.
- CAPA Execution: Develop solutions to eliminate the root cause and prevent recurrence, ensuring alignment with regulatory standards.
- Monitoring & Closure: Assess CAPA efficacy via periodic reviews and audits. Once confirmed effective, the investigation is formally concluded.
Conclusion
Root Cause Analysis (RCA) is indispensable in pharmaceutical quality management, enabling organizations to tackle systemic problems and bolster product integrity. By integrating a rigorous RCA framework, companies can achieve ongoing enhancements, meet regulatory demands, and foster stakeholder trust.
Q&A Section
Q1: What is the primary purpose of Root Cause Analysis (RCA)?
A: RCA aims to uncover the core source of a deviation or non-compliance to implement solutions that prevent recurrence and strengthen quality systems.
Q2: Which tools are commonly utilized during RCA?
A: Frequently used tools include Fishbone Diagrams, the 5 Whys, Fault Tree Analysis, Pareto Charts, and Control Charts.
Q3: How do pharmaceutical firms benefit from RCA?
A: RCA enhances regulatory adherence, reduces operational errors, improves product reliability, and streamlines manufacturing processes.
Q4: How do Corrective and Preventive Actions differ in RCA?
A: Corrective Actions resolve the immediate root cause of a problem, while Preventive Actions focus on eliminating future risks through proactive measures.
